About The Conference
We are excited to announce that the 35th annual Conference on Computational Linguistics and Speech Processing (ROCLING 2023) will be held in Soochow University, Waishuanghsi Campus, Taipei City, Taiwan from October 20-21, 2023. Sponsored by the Association for Computational Linguistics and Chinese Language Processing (ACLCLP), ROCLING 2023 aims to provide an international forum for researchers and industry practitioners to exchange ideas, present original research findings and share practical development experiences from all areas of language and speech research. ROCLING 2023 will feature a range of activities, including oral papers, posters, tutorials, special sessions and shared tasks. The conference covers all language and speech research areas, such as computational linguistics, information understanding and signal processing, and focuses on two scientific tracks: natural language processing (NLP) and speech processing (Speech). The conference is open to papers written in both Chinese and English and encourages researchers and practitioners from around the world to submit their work. The ROCLING conference series was initiated in 1988 by ACLCLP with the aim of providing a platform for researchers and professionals to share their experiences related to natural language processing and speech processing. Since then, the conference has become an important annual event for the computational linguistics and speech processing community.
Where
Soochow University, Waishuanghsi Campus, Taipei City, Taiwan
When
20 (Friday) to 21 (Saturday), October 2023
Important Dates
All deadlines are 11.59 pm UTC/GMT +08:00 (Asia/Taipei)
day, 00 month 0000
Photo
Submission Guidelines
ROCLING 2023 invites paper submissions reporting original research results and system development experiences as well as real-world applications. Each submission will be reviewed based on originality, significance, technical soundness, and relevance to the conference. Accepted papers will be presented orally or as poster presentations. Both oral and poster presentations will be published in the ROCLING 2023 conference proceedings and included in the ACL Anthology. A number of papers will be selected and invited for extension into journal versions and publication in a special issue of the International Journal of Computational Linguistics and Chinese Language Processing (IJCLCLP).
Page Limitation
Papers can be written and presented in either Chinese or English. Papers should be made in PDF format and submitted online through the paper submission system. Submitted papers may consist of 4-8 pages of content, plus unlimited references. Upon acceptance, final versions will be given additional pages of content (up to 9 pages) so that reviewers’ comments can be taken into account.
Relevant topics
ROCLING 2023 mainly targets two scientific tracks: natural language processing and speech processing. The generative artificial intelligence topic is also welcomed.
Natural Language Processing
- Cognitive/Psychological Linguistics
- Discourse and Pragmatics
- Dialogue System
- Information Extraction
- Information Retrieval
- Language Generation
- Machine Translation
- NLP Applications
- Phonology, Morphology and Word Segmentation
- Question Answering
- Resources and Evaluation
- Semantics: Lexical, Sentence-Level, Textual Inference
- Sentiment Analysis
- Summarization
- Syntax: Tagging, Chunking and Parsing
- Others
Speech Processing
- Speech Perception, Production and Acquisition
- Phonetics, Phonology and Prosody
- Analysis of Paralinguistics in Speech and Language
- Speaker and Language Identification
- Analysis of Speech and Audio Signals
- Speech Coding and Enhancement
- Speech Synthesis and Spoken Language Generation
- Speech Recognition
- Spoken Dialog Systems and Analysis of Conversation
- Spoken Language Processing: Retrieval, Translation, Summarization, Resources and Evaluation
- Others
Online submission system
Paper submissions must use the official ROCLING 2023 style templates (Latex and Word) and download here. Submission is electronic, using the EasyChair conference management system. The submission site is available at https://easychair.org/conferences/?conf=rocling2023
As the reviewing will be double-blind, papers must not include authors' names and affiliations. Furthermore, self-references that reveal the author's identity must be avoided. Papers that do not conform to these requirements will be rejected without review. Papers may be accompanied by a resource (software and/or data) described in the paper, but these resources should be anonymized as well.
Accepted Papers
Congratulations on these acceptance of papers for presentation at the ROCLING 2023! We appreciate your contribution to the conference and look forward to your participation. We appreciate your contribution to the conference and look forward to your participation.
- Construction of Message Deliver Service Dialog Systems (#1)
- Sentence-level Revision with Neural Reinforcement Learning (#3)
- Multimodal Speech Training for the Hard of Hearing in Mandarine (#4)
- Is GPT-4 a Good Islamic Expert for Answering Quran Questions? (#5)
- Auxiliary loss to attention head for end to end speaker diarization (#6)
- XFEVER: Exploring Fact Verification across Languages (#7)
- Enhancing Automated English Speaking Assessment for L2 Speakers with BERT and Wav2vec2.0 Fusion (#8)
- Analyzing ChatGPT's Mathematical Deficiencies: Insights and Contributions (#9)
- Taiwanese/Mandarin Speech Recognition using OpenAI's Whisper Multilingual Speech Recognition Engine Based on Generative Pretrained Transformer Architecture (#10)
- An Analysis of “X shi Y” Metaphors in Mandarin Corpora and Learning Materials (#11)
- The Pilot Study and Model Construction for Word Segmentation in Taiwan Hakka (#12)
- Compact CNNs for End-to-End Keyword Spotting on Resource-Constrained Edge AI Devices (#15)
- Improving End-to-end Taiwanese-Speech-to-Chinese-Text Translation by Semi-supervised Learning (#17)
- Addressing the issue of Data Imbalance in Multi-granularity Pronunciation Assessment (#18)
- Category Mapping for Zero-shot Text Classification (#20)
- Sound Processing for Cochlear Implants: The Journey of Innovation Toward Artificial Intelligence (#21)
- ESC MA-SD Net: Effective Speaker Separation through Convolutional Multi-View Attention and SudoNet (#22)
- Leveraging Dialogue Discourse Parsing in a Two-Stage Framework for Meeting Summarization (#23)
- Improving Low-Resource Speech Recognition through Multilingual Fine-Tuning with Language Identifiers and Self-Training (#24)
- Story Co-telling Dialogue Generation via Reinforcement Learning and Knowledge Graph (#25)
- SCU-MESCLab at ROCLING-2023 Shared Task:Named Entity Recognition Using Multiple Classifier Model (#27 MultiNER-Health)
- AaWLoss: An Artifact-aware Weighted Loss Function for Speech Enhancement (#30)
- A Comparative Study of Generative Pre-trained Transformer-based Models for Chinese Slogan Generation of Crowdfunding (#32)
- Application of Deep Learning Technology to Predict Changes in Sea Level (#34)
- WordRank: A Word Ranking based Training Strategy for Abstractive Document Summarization (#35)
- Overview of the ROCLING 2023 Shared Task for Chinese Multi-genre Named Entity Recognition in the Healthcare Domain (#36 MultiNER-Health)
- CrowNER at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: Enhancing NER Task with GPT Paraphrase Augmentation on Sparsely Labeled Data (#37 MultiNER-Health)
- ISLab at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: A Three-Stage NER Model Combining Textual Content and Tagged Semantics (#40 MultiNER-Health)
- Fine-Tuning and Evaluation of Question Generation for Slovak Language (#41)
- The Relevance Identification Between Housing Rental Texts And Legal Provisions (#43)
- Impact of Feature Selection Algorithms on Readability Model (#44)
- Investigating Cross-Institutional Recognition of Cancer Registration Items: A Case Study on Catastrophic Forgetting (#46)
- Phonotactic Constraints on Zhangzhou Onsets (#47)
- Accelerating Hakka Speech Recognition Research and Development Using the Whisper Model (#48 Hakka-ASR)
- Enhancing Automatic Speech Recognition Performance Through Multi-Speaker Text-to-Speech (#49 Hakka-ASR)
- The DMS-ASR System for the Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (#50 Hakka-ASR)
- NSYSU-MITLab Speech Recognition System for Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (#51 Hakka-ASR)
- The North System for Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (#52 Hakka-ASR)
- WhisperHakka: A Hybrid Architecture Speech Recognition System for Low-Resource Taiwanese Hakka (#53 Hakka-ASR)
- The NTNU ASR System for Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (#54 Hakka-ASR)
- The Taiwan AI Labs Hakka ASR System for Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (#55 Hakka-ASR)
- A Preliminary Study on Hakka Speech Recognition by Using the Branchformer (#56 Hakka-ASR)
- The NTNU Super Monster Team (SPMT) system for the Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 - Hakka ASR (#57 Hakka-ASR)
- Whisper Model Adaptation for FSR-2023 Hakka Speech Recognition Challenge (#58 Hakka-ASR)
- KNOT-MCTS: An Effective Approach to Addressing Hallucinations in Generative Language Modeling for Question Answering (#13)
- Can generative models be used to detect hate speech related to body shaming? (#14)
- A Novel Named Entity Recognition Model Applied to Specialized Sequence Labeling (#16)
- Analysis of Chinese Irony on PTT Corpus-Using "Tested Positive" and "Hope" as the Key Words (#19)
- Evaluating Interfaced LLM Bias (#26)
- YNU-HPCC at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: A transformer-based approach for Chinese healthcare NER (#28 MultiNER-Health)
- YNU-ISE-ZXW at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: A Transformer-based Model with LoRA for Chinese Healthcare Named Entity Recognition (#29 MultiNER-Health)
Xingwei Zhang, Jin Wang and Xuejie Zhang - Analyzing Bid-Rigging Related Judicial Cases of Government Procurement Law Using Text Mining Techniques (#31)
- Fine-Grained Argument Understanding with BERT Ensemble Techniques: A Deep Dive into Financial Sentiment Analysis (#33)
- Wangxuelin at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: Intelligent Capture of Chinese Medical Named Entities by LLM: Instruct-Tuning via Entity Extraction-Style Prompts (#38 MultiNER-Health)
- Lexical Complexity Prediction using Word Embeddings (#39)
- Solving Linguistic Olympiad Problems with Tree-of-Thought Prompting (#45)
Camera-Ready Paper Submission Guidelines
To ensure a smooth and successful publication process, please adhere to the following camera-ready paper submission guidelines.
Important Dates
- Camera-ready paper submission deadline: September 15 (Fri), 2023
- Registration deadline: September 15 (Fri), 2023
Paper Length
Your camera-ready paper should not exceed 9 pages (plus unlimited references) in the PDF format.
Paper Format
The template is compatible with popular document preparation systems such as LaTeX and Microsoft Word. Please strictly follow the formatting guidelines provided in the final template
File Format
Submit your camera-ready paper in PDF format.
Paper Content
The first page of the camera-ready version of the accepted paper should bear the items of paper title, author name, affiliation, and email address.
All these items should be properly centered on the top, followed by a concise abstract of the paper. In addition, Chinese manuscript must to write English title, abstract, and keywords.
Author Information
Ensure that the author list in your paper is final and correct, as it will be used for conference materials and proceedings. Changes to the author list after submission will not be allowed.
Copyright Forms
Authors must sign and upload a copyright document, granting the conference organizers the right to publish the paper in the conference proceedings. The copyright form is available for download here.
Submission Instructions
Camera-ready papers should be submitted electronically through the conference submission system, which can be accessed at https://easychair.org/conferences/?conf=rocling2023. Please log in using your existing account and follow the instructions for paper submission. Each item on the forms in submission system must be written in English.
Plagiarism Check
Camera-ready paper must to do plagiarism detection by authorself. Ensure that your submission is original and properly cited.
Registration
At least one author must pay the regular registration fee for each publication paper (including shared tasks). More registration information, please see at here
Programs
All sessions will take place in the First Academic Building (第一教學研究大樓).
Registration Location: 1F Lobby
Opening Ceremony Location: R0101
Coffee Break Location: R0112
Oral Session 1 Location: R0112
Topic: Best Paper Award Candidates
Special Session 1 Location: R0101
Lunch Location: R0112、R0201
ACLCLP Assembly Location: R0101
Oral Session 2 Location: R0112
Topic: NLP Applications
Oral Session 3 Location: R0101
Topic: Thesis Award Winners Presentation
Coffee Break Location: R0112
Banquet
Location: No. 221 Chishan Road Section 2, Shilin District, Taipei, Taiwan
Coffee Break Location: R0112
Lunch Location: R0112、R0201
Poster SessionLocation: R0112
Oral Session 6 Location: R0112
Topic: Information Retrieval
Special Session 2 Location: R0101




Topic: Crafting Human-Centered Chatbots: Bridging the Gaps
Coffee Break Location: R0112
Closing Ceremony Location: R0101
Best Paper Award Winners Announced
Presentation Guidelines
For Oral Presentations:
- For oral presentations, we recommend downloading the ROCLING 2023 slider templates.
- Presentations may be conducted in either English or Chinese.
- Each presentation will be allocated 20 minutes for the presentation itself, included a 4-minute session for questions and answers, and an additional 1-minute break for a change of speakers.
- Presenters are kindly requested to introduce themselves to the session chairs before the commencement of their oral session.
- Each room will be equipped with:
- A laptop computer (Windows OS), which can load PPT and PDF
- A projector
- A shared Internet connection
- an audio system
- The display connectors for the screen are both HDMI and VGA.
- Presenters who want to use their laptop for their presentation must bring their adapter to connect to the HDMI/VGA cable and any audio connectors if they have a non-standard audio-out port.
- Before the session, presenters should inform the session chair and test that their computer and adapter work with the projector in the room.
- A wireless internet connection will be available in the presentation rooms.
For Poster Presentations:
- Posters are in A1 size (59.4 cm wide x 84.1 cm high, or 23.4 inches x 33.1 inches).
- Presenters are advised to mount their posters before the start of the session and dismount them after the end of the session.
- Materials to fix the posters will be available on-site.
Pre-recorded Video Instructions (Expats Only):
- In exceptional circumstances (e.g., when international speakers (foreign business travelers) cannot present live), pre-recorded presentations for oral or poster may be permitted and played during the conference.
- At least 15 minutes and at most 20 minutes. Within that interval, choose a duration you feel will best engage your audience. These include having a video of the presenter in the corner of the slides.
- The maximum volume of video is 200MB.
- The file format of video is *.mp4.
- We recommended a video resolution of at least 720 pixels and an aspect ratio of 16:9.
- Please note that final specifications of the pre-recorded video will be checked, non-compliant video may be requested to be re-recorded.
- Please sent the download link (e.g. Google Drive or Dropbox) of the pre-recorded video to the official email (rocling2023@gmail.com) by October 15. In case of poster sessions, the poster file must also be sent in the same time.
Keynote Speakers
Natural Language Processing

Nancy F. Chen
A*STAR
SeaEval for Multilingual Foundation Models: From Cross-Lingual Alignment to Cultural Reasoning
Abstract
We present SeaEval, a benchmark for multilingual foundation models. In addition to characterizing how these models understand and reason with natural language, we also investigate how well they comprehend cultural practices, nuances, and values. Alongside standard accuracy metrics, we examine the brittleness of foundation models in the dimensions of semantics and multilinguality. Our investigations encompasses both open-source and proprietary models, shedding light on their behavior in classic NLP tasks, reasoning, and cultural contexts. Notably, (1) Most models respond inconsistently to paraphrased instructions. (2) Exposure bias pervades, evident in both standard NLP tasks and cultural understanding. (3) For questions rooted in factual, scientific, or common sense knowledge, consistent responses are expected across multilingual queries that are semantically equivalent. Yet, many models intriguingly demonstrate inconsistent performance on such queries. (4) Models trained multilingually still lack ``balanced multilingual'' capabilities. Our endeavors underscore the need for more generalizable semantic representations and enhanced multilingual contextualization. SeaEval can serve as a launchpad for in-depth investigations for multilingual and multicultural evaluations.
Biography
Nancy F. Chen is an A*STAR fellow, senior principal scientist, principal investigator, and group leader at I2R (Institute for Infocomm Research) and Principal Investigator at CFAR (Centre for Frontier AI Research). Her group works on generative AI in speech, language, and conversational technology. Her research has been applied to education, defense, healthcare, and media/journalism. Dr. Chen has published 100+ papers and supervised 100+ students/staff. She has won awards from IEEE, Microsoft, NIH, P&G, UNESCO, L’Oréal, SIGDIAL, APSIPA, MICCAI. She is an IEEE SPS Distinguished Lecturer (2023-2024), Program Chair of ICLR 2023, Board Member of ISCA (2021-2025), and Singapore 100 Women in Tech (2021). Technology from her team has led to commercial spin-offs and government deployment. Prior to A*STAR, she worked at MIT Lincoln Lab while doing a PhD at MIT and Harvard. For more info: http://alum.mit.edu/www/nancychen.
Speech Processing

Peng-Jen Chen
Meta AI
Building Speech-to-Speech Translation System for English-Hokkien
Abstract
Speech is the primary mode of communication for people who speak languages that lack a standard writing system. With nearly 3000 such unwritten languages in existence, developing speech-to-speech translation technology is critical in overcoming language barriers for these communities. In this talk, we will explore the challenges involved in building a speech-to-speech translation system for English-Taiwanese Hokkien, a real-world language that lacks a widely used standard writing system. We will present our approaches ranging from training data collection and modeling choices, to the evaluation of the developed models.
Biography
Peng-Jen Chen is a research engineer at Meta AI. He received a B.S. degree in 2007 and an M.S. degree in 2009 in Computer Science and Information Engineering, at National Taiwan University. He joined Meta as a machine learning engineer in 2012 and joined FAIR as a research engineer in 2018. His key research interests include low-resource machine translation, speech-to-speech translation, speech-text joint pre-training.
Special Session
ROCLING 2023 will feature two special sessions that provide a novel topics for participants to know the trend on large language model (LLM).
Special Session 1:
Techniques for Large Language Models
我們與語音版 ChatGPT 的距離
李宏毅 Hung-Yi Lee
Associate Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering and the Department in Computer Science & Information Engineering of National Taiwan University
Abstract
在過去的幾個月裡,大型語言模型如ChatGPT的能力已經引起了大眾的廣泛討論和驚嘆,這些語言模型具有通用的處理能力,僅需給予正確的指令,往往就可以完成任務。然而,我們與語音版的ChatGPT的距離還有多遠?我們還缺少什麼才能實現語音版的ChatGPT的誕生?在這場演講中,我將分享一系列可能引領我們走向語音版ChatGPT的最新研究成果,並探討目前的挑戰、潛在的解決方案,讓我們一起攜手迎接由語音版ChatGPT帶來的未來新紀元。
Towards Human-Like Conversational AI
陳縕儂 Yun-Nung Chen
Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering in National Taiwan University
Abstract
This talk explores two crucial dimensions of Conversational AI: improved understanding and enhanced interaction. The talk will begin with a focus on refining language comprehension through the mitigation of speech recognition errors, ultimately facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of user inputs. Next, we tackle the challenge of scalability, uncovering strategies to maximize the utility of limited dialogue data, thereby enabling adaptive conversational models. Finally, we explore the realm of enriched interaction by seamlessly integrating recommendation systems into conversational interfaces. In sum, These dimensions collectively showcase the potential for substantial progress in Conversational AI, offering valuable insights for future research and innovation in the field.
Biography
Yun-Nung (Vivian) Chen is currently an associate professor in the Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering at National Taiwan University. She earned her Ph.D. degree from Carnegie Mellon University, where her research interests focus on spoken dialogue systems and natural language processing. She was recognized as the Taiwan Outstanding Young Women in Science and received Google Faculty Research Awards, Amazon AWS Machine Learning Research Awards, MOST Young Scholar Fellowship, and FAOS Young Scholar Innovation Award. Her team was selected to participate in the first Alexa Prize TaskBot Challenge in 2021. Prior to joining National Taiwan University, she worked in the Deep Learning Technology Center at Microsoft Research Redmond.
Special Session 2:
Crafting Human-Centered Chatbots: Bridging the Gaps
Natural language processing (NLP) technology has advanced by leaps and bounds, and chatGPT has been widely loved by netizens since it was launched on the market since last November. Due to the shortage of manpower, the need for dialogue systems is greater than ever. However, creating a dialogue system that can interact with users in accordance with given tasks (such as syllabus, medical orders, health education) is still a considerable challenge. When an agent is given a certain task (such as teaching goal or consulting), how to guide the user to complete the goal requires more human-centered design thinking. "Crafting Human-Centered Chatbots: Bridging the Gaps" forum serves as a gathering place for professionals, researchers, and enthusiasts passionate about the development and deployment of chatbots. Here, we will explore the intricacies of designing chatbots that bridge the gaps between technology and human engagement.
Chair
張嘉惠 Chia-Hui Chang
Professor, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering in National Central University
Panelists
心理諮商對話系統的開發
簡仁宗 Jen-Tzung Chien
Chair Professor, Institute of Electrical and Computer Engineering in National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
沉浸式視覺設計互動系統
古倫維 Lun-Wei Ku
Research Fellow/Professor, Institute of Information Science in Academia Sinica
教育類型對話系統的開發
劉晨鐘 Chen-Chung Liu
Chair Professor, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering at National Central University
從物理課的虛擬助教到人社領域的指令工程:AIGC應用於清華大學的嘗試
王道維 Daw-Wei Wang
Director of Counselling Center, and Vice Director of Center for Application and Development of AI in HSS
Professor in Physics Department, National Tsing-Hua University
Shared Tasks
ROCLING 2023 will feature two shared tasks that provide an opportunity for participants to showcase their expertise and innovative approaches in tackling specific challenges. Let's take a closer look at each shared task:
Shared Task 1: MultiNER-Health
Chinese Multi-genre Named Entity Recognition in the Healthcare Domain
Organizers
李龍豪 Lung-Hao Lee
國立中央大學電機工程學系
Department of Electrical Engineering in National Central University
lhlee@ee.ncu.edu.tw
林孜彌 Tzu-Mi Lin
國立中央大學電機工程學系
Department of Electrical Engineering in National Central University
110521087@cc.ncu.edu.tw
陳昭沂 Chao-Yi Chen
國立中央大學電機工程學系
Department of Electrical Engineering in National Central University
110581007@cc.ncu.edu.tw
Registration
Please fill the registration form: here. Organizers will confirm your registration and add all registrants to the google groups.
Contact
Please join our Google group for direct communication at rocling23-shared-task@googlegroups.com.
I. Background
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a fundamental task in information extraction that locates the mentions of named entities and classifies them (e.g., person, organization and location) in unstructured texts. The NER task has traditionally been solved as a sequence labeling problem, where entity boundaries and category labels are jointly predicted. Chinese NER is more difficult to process than English NER. Chinese language is logographic and provides no conventional features like capitalization. In addition, due to a lack of delimiters between characters, Chinese NER is correlated with word segmentation, and named entity boundaries are also word boundaries. However, incorrectly segmented entity boundaries will cause error propagation in NER. For example, in a particular context, a disease entity “思覺失調症” (schizophrenia) may be incorrectly segmented into three words: “思覺” (thinking and feeling), “失調” (disorder) and “症” (disease).
In the digital era, healthcare information-seeking users usually search and browse web content in click-through trails to obtain healthcare-related information before making a doctor’s appointment for diagnosis and treatment. Web texts are valuable sources to provide healthcare information such as health-related news, digital health magazines and medical question/answer forums. Domain-specific healthcare information includes many proper names, mainly as named entities, such as “葡萄糖六磷酸鹽去氫酶” (Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase; G6PD), “電腦斷層掃描” (computed tomography; CT), and “靜脈免疫球蛋白注射” (intravenous immunoglobulin; IVIG). In summary, Chinese healthcare NER is an important and essential task in natural language processing to automatically identify healthcare entities such as symptoms, chemicals, diseases, and treatments for machine reading and understanding.
Following the ROCLING-2022 shared task focused on Chinese healthcare NER, we organize a MultiNER-Health shared task for multi-genre NER in the healthcare domain. In this shared task, we have three genres:
- Formal texts (FT): this includes health news and articles written by professional editors or journalists.
- Social media (SM): this contains texts from crowed users in medical question/answer forums.
- Wikipedia articles (WA): this free online encyclopedia includes articles created and edited by volunteers worldwide
Named entities may be used in different word forms in other genres. For example, “後天免疫缺乏症候群” (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome; AIDS) is commonly used as a spoken language form “愛滋病” in the medical forums. On the other hand, “甘油三酯” is a different usage referred to as “三酸甘油酯” (triglyceride; TG) in Wikipedia.
II. Task Description
A total of 10 entity types are described and some examples are provided in Table I for Chinese healthcare NER. In this task, participants are asked to predict the named entity boundaries and categories for each given sentence. We use the common BIO (Beginning, Inside, and Outside) format for NER tasks. The B-prefix before a tag indicates that the character is the beginning of a named entity and I-prefix before a tag indicates that the character is inside a named entity. An O tag indicates that a token belongs to no named entity. Below are the example sentences.
Table 1. Named Entity Types
| Entity Type | Description | Examples |
| Body (BODY) |
The whole physical structure that forms a person or animal including biological cells, organizations, organs and systems. | “細胞核” (nucleus), “神經組織” (nerve tissue), “左心房” (left atrium), “脊髓” (spinal cord), “呼吸系統” (respiratory system) |
| Symptom (SYMP) |
Any feeling of illness or physical or mental change that is caused by a particular disease. | “流鼻水” (rhinorrhea), “咳嗽” (cough), “貧血” (anemia), “失眠” (insomnia), “心悸” (palpitation), “耳鳴” (tinnitus) |
| Instrument (INST) |
A tool or other device used for performing a particular medical task such as diagnosis and treatments. | “血壓計” (blood pressure meter), “達文西手臂” (DaVinci Robots), “體脂肪計” (body fat monitor), “雷射手術刀” (laser scalpel) |
| Examination (EXAM) |
The act of looking at or checking something carefully in order to discover possible diseases. | “聽力檢查” (hearing test), “腦電波圖” (electroencephalography; EEG), “核磁共振造影” (magnetic resonance imaging; MRI) |
| Chemical (CHEM) |
Any basic chemical element typically found in the human body. | “去氧核糖核酸” (deoxyribonucleic acid; DNA), “糖化血色素” (glycated hemoglobin), “膽固醇” (cholesterol), “尿酸” (uric acid) |
| Disease (DISE) |
An illness of people or animals caused by infection or a failure of health rather than by an accident. | “小兒麻痺症” (poliomyelitis; polio), “帕金森氏症” (Parkinson’s disease), “青光眼” (glaucoma), “肺結核” (tuberculosis) |
| Drug (DRUG) |
Any natural or artificially made chemical used as a medicine. | “阿斯匹靈” (aspirin), “普拿疼” (acetaminophen), “青黴素” (penicillin), “流感疫苗” (influenza vaccination) |
| Supplement (SUPP) |
Something added to something else to improve human health. | “維他命” (vitamin), “膠原蛋白” (collagen), “益生菌” (probiotics), “葡萄糖胺” (glucosamine), “葉黃素” (lutein) |
| Treatment (TREAT) |
A method of behavior used to treat diseases. | “藥物治療” (pharmacotherapy), “胃切除術” (gastrectomy), “標靶治療” (targeted therapy), “外科手術” (surgery) |
| Time (TIME) |
Element of existence measured in minutes, days, years. | “嬰兒期” (infancy), “幼兒時期” (early childhood), “青春期” (adolescence), “生理期” (on one’s period), “孕期” (pregnancy) |
Table 2. Shared Task Examples
| Genre | Examples | Input & Output |
| Formal Texts |
Ex 1 | Input: 早起也能預防老化,甚至降低阿茲海默症的風險 Output: O, O, O, O, O, O, B-SYMP, I-SYMP, O, O, O, O, O, B-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, O, O, O |
| Ex 2 | Input: 壓力、月經引起的痘痘患者 Output: B-SYMP, I-SYMP, O, B-TIME, I-TIME, O, O, O, B-DISE, I-DISE, O, O |
|
| Social Media |
Ex 3 | Input: 如何治療胃食道逆流症? Output: O, O, O, O, B-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, I-DISE, O |
| Ex 4 | Input: 請問長期打善思達針劑是不是會變胖? Output: O, O, O, O, O, B-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, O, O, O, O, B-SYMP, I-SYMP, O? |
|
| Wikipedia Articles |
Ex 5 | Input: 抗生素和維生素A酸可用於口服治療痤瘡 Output: B-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, O, B-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, I-DRUG, B-DRUG, O, O, O, O, O, O, O, B-DISE, I-DISE (“痤瘡” is a formal usage of “痘痘” in the example 2 ) |
| Ex 6 | Input: 抑酸劑,又稱抗酸劑,抑制胃酸分泌,緩解燒心。 Output: B-CHEM, I-CHEM, I-CHEM, O, O, O, B-CHEM, I-CHEM, I-CHEM, O, O, O, B-CHEM, I-CHEM, O, O, O, O, O, B-DISE, I-DISE, O (“燒心” is the spoken language of “胃食道逆流症” in the example 3 ) |
III. Data
| Training Set | |||
| Genre | Formal Texts | Social Media | Wikipedia Articles |
| #Sentences | 23,008 | 7,684 | 3,205 |
| #Characters | 1,109,918 | 403,570 | 118,116 |
| #Named Entities | 42,070 | 26,390 | 13,369 |
| Data Sets | Chinese HealthNER Corpus (Lee and Lu, 2021) |
CHNER Dataset (Lee et al., 2022) |
|
Notes: The policy of this shared task is an open test. Participating systems are allowed to use other publicly available data for this shared task, but the use of other data should be specified in the final system description paper.
Testing SetTesting Set at least 2,000 Chinese sentences per genre will be provided for system performance evaluation.
IV. Evaluation
The performance is evaluated by examining the difference between machine-predicted labels and human-annotated labels. We adopt standard precision, recall, and F1-score, which are the most typical evaluation metrics of NER systems at a character level. If the predicted tag of a character in terms of BIO format was completely identical with the gold standard, that is one of the defined BIO tags, the character in the testing instance was regarded as correctly recognized. Precision is defined as the percentage of named entities found by the NER system that are correct. Recall is the percentage of named entities present in the test set found by the NER system. Different genre will be evaluated independently. The Macro-averaging F1 score among three genres will be used for final ranking in the leaderboard.
V. Results
| Team | Run# | F1-score (%) | Rank | |||
| Formal Texts | Social Media | Wikipedia Articles | Macro-averaging | |||
| CrowNER [1] | Run 2 | 65.49 | 69.54 | 73.63 | 69.55 | 1 |
| YNU-HPCC [2] | Run 2 | 61.96 | 71.11 | 72.13 | 68.40 | 2 |
| ISLab [3] | Run 1 | 62.52 | 71.42 | 71.19 | 68.38 | 3 |
| SCU-MESCLab [4] | Run 1 | 62.51 | 71.33 | 70.57 | 68.14 | 4 |
| YNU-ISE-ZXW [5] | Run 3 | 62.79 | 70.22 | 70.37 | 67.79 | 5 |
| LingX [6] | Run 2 | 51.23 | 59.28 | 60.54 | 57.02 | 6 |
| Baseline [7] (BiLSTM-CRF) |
Word2vec | 60.99 | 67.16 | 67.91 | 65.35 | - |
| BERT | 61.08 | 70.77 | 72.54 | 68.13 | - | |
- Yin-Chieh Wang, Wen-Hong Wu, Feng-Yu Kuo, Han-Chun Wu, Te-Yu Chi, Te-Lun Yang, Sheh Chen, and Jyh-Shing Roger Jang. 2023. CrowNER at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: enhancing NER task with GPT paraphrase augmentation on sparsely labeled data.
- Chonglin Pang, You Zhang, and Xiaobing Zhou. YUN-HPCC at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: a transformer-based approach for Chinese healthcare NER.
- Jun-Jie Wu, Tao-Hsing Chang, and Fu-Yuan Hsu. 2023. ISLab at ROCLING 2023. MultiNER-Health Task: a three-stage NER model combining textual content and label semantics.
- Tzu-En Su, Ruei-Cyuan Su, Ming-Hsiang Su, and Tsung-Hsien Yang. 2023. SCU-MESCLab at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: named entity recognition using multiple classifier model.
- Xingwei Zhang, Jin Wang, and Xuejie Zhang. 2023. YUN-ISE-ZXW at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: a transformer-based model with LoRA for Chinese healthcare named entity recognition.
- Xuelin Wang and Qihao Yang. 2023. LingX at ROCLING 2023 MultiNER-Health Task: intelligent capture of Chinese medical named entities by LLMs.
- Lung-Hao Lee, Chien-Huan Lu, and Tzu-Mi Lin. 2022. NCUEE-NLP at SemEval-2022. Task 11: Chinese named entity recognition using the BERT-BiLSTM-CRF model. In Proceedings of the 16th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation. Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 1597-1602.
VI. Important Date
- Release of training data: April 15, 2023
- Shared task registration due: July 25, 2023
- Release of test data: August 1, 2023
- Testing results submission due: August 3, 2023
- Release of evaluation results: August 7, 2023
- System description paper due: August 25, 2023
- Notification of acceptance: September 8, 2023
- Camera-ready deadline: September 15, 2023
- Main conference: October 20-21, 2023
VII. Baseline System
We provide a starter kit on our GitHub Repo. It can be used to create the BiLSTM-CRF system for the NER tasks.
https://github.com/NCUEE-NLPLab/AITutorial-2022-ChineseNER
References
Lung-Hao Lee, and Yi Lu (2021). Multiple Embeddings Enhanced Multi-Graph Neural Networks for Chinese Healthcare Named Entity Recognition. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (IEEE JBHI), 25(7): 2801- 2810.
Lung-Hao Lee, Chao-Yi Chen, Liang-Chih Yu, and Yuen-Hsien Tseng (2022). Overview of the ROCLING 2022 Shared Task for Chinese Healthcare Named Entity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Computational Linguistics and Speech Processing (ROCLING'22), pp. 363-368.
Shared Task 2:
Formosa Speech Recognition Challenge 2023 (Hakka ASR)
2023客語語音辨認競賽
Organizers
Hakka Affairs Council
Industry Academia Innovation School, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
Co-Organizers
The Association for Computational Linguistics and Chinese Language Processing
National Center for High-Performance Computing
I. Background of the Competition Event
In order to sustainably inherit the Hakka language, accelerate research and development in Hakka speech recognition, and promote the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database established by our organization, we are organizing the "2023 Hakka Speech Recognition Competition" to provide the existing Taiwan Hakka Speech Database as a basis for training speech recognition models for competition participants. Through this series of competitions, we aim to expedite domestic research and development in Hakka speech recognition and promote academic research and industrial development in Hakka speech AI.
The competition is organized by Hakka Affairs Council and Industry Academia Innovation School, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University. It is co-organized by The Association for Computational Linguistics and Chinese Language Processing and National Center for High-Performance Computing. Based on Hakka Affairs Council's speech database, we will provide training data for speech recognition models to competition participants, with the goal of injecting technological energy into the practical use of Hakka in daily life, promoting Hakka language and culture, and enhancing the popularization of Hakka usage.
II. Event Schedule and Competition Registration
| Date | Event |
| June 5th to July 31st, 2023 | Registration period |
| August 7th, 2023 | Warm-up round (non-scoring) |
| September 11th, 2023 | Final round |
| October 20th, 2023 | Award ceremony and certificate presentation (physical event) |
| October 20th to 21st, 2023 | Presentation of results at ROCLING 2023 Conference |
- The competition is open to all and registration is free of charge.
- Registration will begin on June 5th, 2023, and end on July 31st, 2023 (please refer to the third point below for the required documents for registration). There are two categories for competition: the General Category (for members of the public) and the Student Category. Each team can have a maximum of 5 members, or individuals can register on their own. Each person can only participate in one team and cannot be part of multiple teams. It is required to designate one team member as the main contact person for communication.
- In order to participate in the competition and obtain the authorization to use the "Taiwan Hakka Speech Database" provided by the Hakka Affairs Council, the following requirements must be fulfilled:
- Completion and signing of the "Intellectual Property Protection and Confidentiality Consent Agreement for the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database" issued by the Hakka Affairs Council. The signed agreement should be sent via email to the designated team email address: SARC@nycu.edu.tw. The email should include the team name, name of the main contact person, and contact information. Once the data verification is completed by the organizing committee and confirmed to be correct, a notification email confirming successful registration will be sent. Upon receipt of the confirmation email, the registration process will be considered complete, and the email will also provide a password to download the relevant data from the website.
- Submission of the recognition results, corresponding scores, and a description of the recognition system for both the warm-up round and the final round test audio files. These results should be submitted via email to the designated team email address: SARC@nycu.edu.tw. The deadline for submission is August 14th and September 22nd respectively. Additionally, a preliminary draft of the paper must be submitted by September 22nd.
- Completion of paper revisions and submission to the ROCLING 2023 Conference by October 6th.
- The authorized use of the Hakka speech data is strictly limited to academic research and technical development and cannot be transferred to third parties or used for commercial purposes. If the above requirements cannot be fulfilled, all Hakka speech data files and related materials from the "Taiwan Hakka Speech Database" must be immediately and completely deleted.
- The registration period starts on June 5th and ends on July 31st, with the release of 60 hours of Hakka speech data files (including audio files and transcripts) from the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database. Participating teams are required to use the provided corpora and recognition module from the organizers to train and develop their own speech recognizer.
- On August 7th, there will be a warm-up round:
- There will be two competition categories: □ transcription to Hakka Chinese characters □ transcription to Hakka Pinyin. Participants can choose at least one category, and they can also participate in both categories simultaneously. The results of the recognition should be submitted before August 14th.
- During the warm-up round, 10 hours of Hakka speech data files (audio files only) from the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database will be released.
- The organizers will announce the answers and participants' submissions on the competition website before August 21st.
- Please follow the specified format for submission: Use "Organization + Team Name + Participant" as the filename, and the answer should be in the format of ID Answer (with one column for the audio file ID and one column for the output of the speech recognizer)
- On September 11th, the final round of the competition will take place:
- There will be two competition categories: □ transcription to Hakka Chinese characters □ transcription to Hakka Pinyin. Participants can choose at least one category, and they can also participate in both categories simultaneously. The results of the recognition should be submitted along with the preliminary draft of the paper before September 22nd.
- During the final round, 10 hours of Hakka speech data files (audio files only) from the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database will be released.
- The organizers will evaluate the submitted data and announce the answers and participants' submissions on the competition website before September 29th.
- Please follow the specified format for submission: Use "Organization + Team Name + Participant" as the filename, and the answer should be in the format of ID Answer (with one column for the audio file ID and one column for the output of the speech recognizer).
- Participants are required to complete the revision of their papers and submit them to the ROCLING 2023 Conference before October 6th.
- The organizers reserve the right to make adjustments to the content and schedule of the competition. Any updates or changes will be announced primarily on the competition website.
III. The evaluation process for the competition is as follows:
- Submission of Materials: Each participating team is required to submit the recognition results of the test audio files, description of the recognition system, and the paper report within the given deadline.
- Since only audio files are provided for the warm-up and final rounds, the evaluation will be based on the recognition results submitted by the participating teams. A judging panel, consisting of members from the research team, will use the provided transcripts of the audio files as the reference answers and calculate the error rates according to the following systems.
- The evaluation methods for the two competition categories are as follows:
- Track 1: Transcription to Hakka Chinese characters - Calculate the Character Error Rate (CER).
- Track 2: Transcription to Hakka Pinyin - Calculate the Syllable Error Rate (SER).
- In the final round, the ranking will be determined separately for each competition category based on the recognition rates to determine the highest-performing participants.
IV. Awards and Event Achievements
- Certificates will be awarded to the participating teams upon completion of the competition. Specifically, certificates will be presented for the following four categories: Student Group - Hakka Characters, Student Group - Hakka Pinyin, General Group - Hakka Characters, and General Group - Hakka Pinyin. Each category will have a first-place certificate awarded (depending on the actual number of participating teams, consideration may be given to awarding second and third-place certificates). The certificate presentation ceremony is scheduled for October 20th, 112th year.
- From October 20th to 21st, ROCLING 2023 will feature presentations of relevant research achievements.
V. Participation Notice
- By participating in the competition, the teams are considered to agree to the rules and regulations of the event. In case of any disputes, the organizer reserves the right of final interpretation. Any disputes will be handled in accordance with the laws of the Republic of China, and the Taipei District Court shall have jurisdiction as the court of first instance.
- Registration and Personal Rights:
- The information provided during registration must be accurate and must not involve the impersonation or theft of anyone's data. If there is any false or incorrect information, the organizer may cancel the team's participation and eligibility for winning. If any damage is caused to the organizer or any other person's rights, all team members shall bear the relevant legal responsibilities.
- Collection of Participants' Personal Information:
- The organizer and co-organizer will conduct the Hakka speech recognition competition and obtain personal information from participants/teams that is submitted in the "Intellectual Property Protection and Confidentiality Consent Form for the Establishment of the Taiwan Hakka Speech Database" or other personal information that can be directly or indirectly identified.
- Participants/teams consent to the retention of the above-mentioned personal information by the organizer for the management needs of the competition (such as system operation management, notification and contact, award certificates, event information dissemination, relevant statistical analysis, etc.).
- Other considerations:
If there are any matters not covered in these event regulations, the organizer reserves the right to modify and supplement any changes, updates, or modifications to the event, in accordance with relevant legal provisions. The official announcements on the event website shall serve as the basis for such modifications and updates.
VI. Contact Information for this Competition:
- Ms. Yang: 03-5712121#54554 / m31221123@nycu.edu.tw
- Ms. Bai: 03-5712121#54555 / pehsimju@nycu.edu.tw
VII. The organizer reserves the right to cancel, terminate, modify, or suspend this event at any time.
主辦單位
客家委員會
國立陽明交通大學產學創新研究學院
協辦單位
社團法人中華民國計算語言學學會
財團法人國家實驗研究院國家高速網路與計算中心
一、 競賽活動緣起
為永續傳承客家語言,加速客語語音辨識研究及發展,並推廣本會建置之臺灣客語語音資料庫,讓更多團隊投入客語語音開發,特辦理「2023客語語音辨認競賽活動」,規劃以現有臺灣客語語音資料庫之語音資料為基礎,提供予競賽學員進行語音辨識模型之訓練。透過此系列競賽加速國內客語語音辨識研究與產業開發進程,推動客語語音AI的學術研究與產業開發。
本次客語語音辨認競賽主辦單位為客家委員會與國立陽明交通大學產學創新研究學院,協辦單位為社團法人中華民國計算語言學學會及財團法人國家實驗研究院國家高速網路與計算中心。擬以客委會語音資料庫為基礎,提供予競賽學員進行語音辨識模型之訓練,期許能透過本活動讓客語在生活使用中注入科技能量,推廣客家語言文化並提升客語使用之普及性。
二、 活動時程及競賽報名辦法
| 時間 | 活動內容 |
| 112年6月5日至7月31日 | 報名期間 |
| 112年8月7日 | 熱身賽(不計算成績) |
| 112年9月11日 | 決賽 |
| 112年10月20日 | 頒獎典禮頒發獎狀(實體活動) |
| 112年10月20至21日 | ROCLING 2023研討會上發表成果 |
- 本競賽不限資格,免費報名
- 112年6月5日開始報名至7月31日截止(報名應備文件詳見以下第三點),分為一般組(社會人士)及學生組競賽,每隊上限5人或個人報名皆可,每人僅可參加1個隊伍,無法重複組隊,並須推派1位團隊主要聯絡人擔任窗口聯繫。
- 報名競賽需全程參與本活動,始能獲得「客家委員會」授權「臺灣客語語音資料庫」之客語語音語料音檔,詳述如下:
- 須完成「客家委員會建置臺灣客語語音資料庫智慧財產保護暨保密同意書」簽署,並於信件中署名隊伍名稱、主要聯絡人姓名及聯繫方式寄回工作小組信箱SARC@nycu.edu.tw,待工作小組完成資料驗證並確認無誤後將會寄回報名成功通知信件,收到確認信件後始完成報名程序,信件內將一併提供密碼可至網站下載相關資料。
- 須分別於112年8月14日及9月22日前繳回熱身賽及決賽測試音檔的辨認結果、與結果相對應之辨認分數、辨認系統描述說明至工作小組信箱SARC@nycu.edu.tw(9月22日前亦須一併繳交論文初稿)。
- 須於10月6日前完成論文修改並投稿至ROCLING 2023研討會。
- 本活動授權客語語音語料不得轉授權予第三人且僅供學術研究及技術開發,禁止用於商業用途。倘無法完成上述要件,須即時完整刪除所有「臺灣客語語音資料庫」之客語語音語料音檔及相關資料。
- 112年6月5日至7月31日開始報名&釋放臺灣客語語音資料庫之客語語音語料音檔60小時(含音檔及文字稿):參賽隊伍需透過主辦單位提供的語料及辨識模組訓練並完成自己的語音辨認器。
- 112年8月7日熱身賽::
- 2個競賽項目分別為將音檔轉出□客語漢字、□客語拼音(至少擇1項,亦可同時參加),並於8月14日前繳交其辨認結果。
- 釋放臺灣客語語音資料庫之客語語音語料音檔10小時 (僅釋放音檔)。
- 主辦單位將於8月21日前公告答案及參賽隊伍繳交成果於競賽官網中(不計算成績)。
- 繳交格式:檔名請以「單位+隊名+參賽者」為檔名;答案格式:ID 答案(一欄為音檔ID,一欄為語音辨認器輸出)。
- 112年9月11日決賽:
- 2個競賽項目分別為將音檔轉出□客語漢字、□客語拼音,(至少擇1項,亦可同時參加),並於9月22日前繳交其辨認結果及論文初稿。
- 釋放臺灣客語語音資料庫之客語語音語料音檔10小時(僅釋放音檔)。
- 主辦單位就回收之資料進行評分並於9月29日前公告答案及參賽隊伍繳交成果於競賽官網中。
- 繳交格式:檔名請以「單位+隊名+參賽者」為檔名;答案格式:ID 答案(一欄為音檔ID,一欄為語音辨認器輸出)。
- 於10月6日前完成論文修改並投稿至ROCLING 2023研討會。
- 主辦單位保有調整內容及時間之權利,相關內容以網站公告為主
三、 評分方式
- 交付資料:各參賽隊伍須在期限前繳交測試音檔的辨認結果、辨認系統描述說明及論文報告。
- 由於熱身及決賽僅釋放音檔,評分方式為參賽隊伍繳交其辨認結果,由研究團隊成員組成評審工作小組,分別針對2個競賽項目以客委會提供之音檔文字稿為標準答案並以下列系統計算錯誤率進行評分。
- 2個競賽項目評分方式如下:
- Track1將音檔轉出客語漢字:計算CER(字元錯誤率)。
- Track2將音檔轉出客語拼音:計算SER(音節錯誤率)。
- 決賽將分別就2個競賽項目進行該辨識率高低排序進行排名。
四、 頒獎及活動成果
- 頒發參賽隊伍完賽獎狀,並分別頒發學生組客語漢字組別、學生組客語拼音組別及一般組客語漢字組別、一般組客語拼音組別共計4個組別第一名獎狀,(屆時將視實際參賽隊伍數量考量是否頒發第二、三名獎狀),並訂於112年10月20日頒發獎狀。
- 112年10月20至21日ROCLING 2023中發表相關研究成果。
五、 參賽須知
- 參賽隊伍參與競賽,視同同意活動辦法及各項規定,若有任何爭議,主辦單位保有最終解釋權,任何有關之爭議,均依中華民國法律處理,並以臺灣臺北地方法院為第一審管轄法院。
- 報名與個人權益:
- 報名所填寫之資料必須詳實,不可冒用或盜用任何人之資料。如有不實或不正確之情事,主辦單位得取消參賽及得獎資格。如有致損害於主辦單位或其他任何人之相關權益,參賽隊伍全體隊員應自負相關法律責任。
- 蒐集參賽者個人資料告知事項:
- 主辦單位與協辦單位,辦理客語語音辨認競賽活動,獲取參賽者/參賽隊伍回傳客家委員會建置臺灣客語語音資料庫智慧財產保護暨保密同意書上之個人資料,或其他得以直接或間接識別之個人資料。
- 參賽者/參賽隊伍同意留存上述相關個人資料作為主辦單位管理競賽需要之用( 例如:系統作業管理、通知聯繫、得獎證書、活動訊息發佈、相關統計分析等使用 )。
- 其它注意事項:
本活動辦法如有未盡事宜,除依法律相關規定外,主辦單位保留修改及補充包括活動之任何異動、更新、修改之權利,並以本活動網站公告為依據。
六、 本競賽活動聯絡窗口
- 楊小姐: 03-5712121#54554 / m31221123@nycu.edu.tw
- 白小姐: 03-5712121#54555 / pehsimju@nycu.edu.tw
七、 主辦單位保留隨時取消、終止、變更或暫停本案之權利
AI Tutorial
ROCLING 2023 will include two AI tutorials that offer participants new insights into the latest trends in Graph Neural Network (GNN).
AI Tutorial I:
Demystifying Graph Neural Networks: Essentials, Applications, and Trends
李政德 Cheng-Te Li
Professor, Institute of Data Science and Department of Statistics of National Cheng Kung University
AI Tutorial II:
Chaining Language and Knowledge Resources with LLM(s)
謝舒凱 Shu-Kai Hsieh
Professor, Graduate Institute of Linguistics &Graduate Institute of Brain and Mind, College of MedicineNational Taiwan University
Abstract
Registrations
Time Zone: UTC/GMT +08:00 (Asia/Taipei)
Early
Registrations
Before September 15, 2023
Regular
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 4,000
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 5,000
Student
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 1,500
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 2,000
Late
Registrations
September 16 - October 10, 2023
Regular
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 4,300
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 5,300
Student
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 1,800
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 2,300
On-Site
Registrations
October 20 - 21, 2023
Regular
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 4,500
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 5,500
Student
- ACLCLP Member: NT$ 2,000
- ACLCLP Non-Member: NT$ 2,500
註冊說明
- 一般參與者且不具學生身份者需註冊 Regular Fee。一般參與者且具學生身份者可選擇註冊 Student Fee。
- 每篇會議論文(包含shared tasks)的發表至少要有一位作者在早鳥註冊截止前繳交一般報名費 (regular fee)。
- 報名費含大會紀念品、午餐、茶點及晚宴,報名費一經繳費後恕不接受退費,會後將郵寄相關資料予報名者。
- ACLCLP Member 為「中華民國計算語言學學會」之有效會員。
- 本年度尚未繳交年費之舊會員或失效之會員,與會身份/Category請勾選「….(會員+會費)」,勿再重複申請入會。
- 非會員欲同時申請入會者,請先至學會網頁之「會員專區」申請加入會員;報名時「與會身份/Category」請勾選「….(會員+會費)」。(前往會員專區)
- 以「學生新會員」及「學生非會員」身份報名者,請於報名時上傳學生身份證明。
- 贊助單位敬請於10月6日前完成報名手續。
- 報名費收據將於會議當日報到時交付。
Registration Details
- A regular fee must be paid by the general participants (not a student). Students (general participants) can choose to pay the student fee.
- Before early registration due, each publication paper (including shared tasks) must have at least one author pay a regular fee.
- Registration fee includes: abstract booklet, lunches, coffee breaks, and banquet. Registration fees are non-refundable.
- International registrants have to pay by credit card only (Visa or MasterCard). Receipt will be provided on-site.
- A copy of a valid student ID must be uploaded into the system when registering as a student.
- Sponsor should be registed before October 10 .
報名及繳費期限
- Early Registration: 9/15 (Fri) 以前,報名費應於 9/22 (Fri)前繳交。
- Late Registration: 9/16 (Fri) 至 10/10 (Tue),報名費應於 10/13 (Fri) 前繳交(報名費加收300元),線上刷卡繳費者需於 10/10 (Tue) 前完成繳費。
- On-Site Registration: 10/10 (Tue) 線上報名截止,擬參加者,請至大會現場報名(報名費加收500元)。
Important Dates for Registration
- Early Registration due by September 15 (Fri) . Payment must be received before September 22.
- Registration between September 16 and October 10. Payment must be received before October 13.
- The registration site will be closed on October 10. After that, please register on-site.
Methods of Payment
-
郵政劃撥/Postal
戶名:中華民國計算語言學學會
帳號:19166251
同一單位多位報名者可合併劃撥,請於劃撥通訊欄中註明「ROCLING及註冊編號或報名者姓名」 - 線上刷卡繳費/credit card on-line。
For registration inquiries, please contact
- 聯絡人:何婉如 小姐(中華民國計算語言學學會/ACLCLP)
- E-mail:aclclp@aclclp.org.tw
- Phone Number: 02-27881638
Organization
Honorary Chair

Wei-Ta Pan
Soochow University
Conference Chairs

Jheng-Long Wu
Soochow University
jlwu@gm.scu.edu.tw

Ming-Hsiang Su
Soochow University
huntfox.su@gmail.com
Program Chairs

Hen-Hsen Huang
Academia Sinica
hhhuang@iis.sinica.edu.tw

Yu Tsao
Academia Sinica
yu.tsao@citi.sinica.edu.tw
Publication Chair

Hou-Chiang Tseng
National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
tsenghc@mail.ntust.edu.tw
Special Session Chair

Chia-Hui Chang
National Central University
chiahui@g.ncu.edu.tw
Shared Task Chairs

Lung-Hao Lee
National Central University
lhlee@ee.ncu.edu.tw

Yuan-Fu Liao
National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
yfliao@nycu.edu.tw
AI Tutorial Chair

Wei-Yun Ma
Academia Sinica
ma@iis.sinica.edu.tw
Organized by
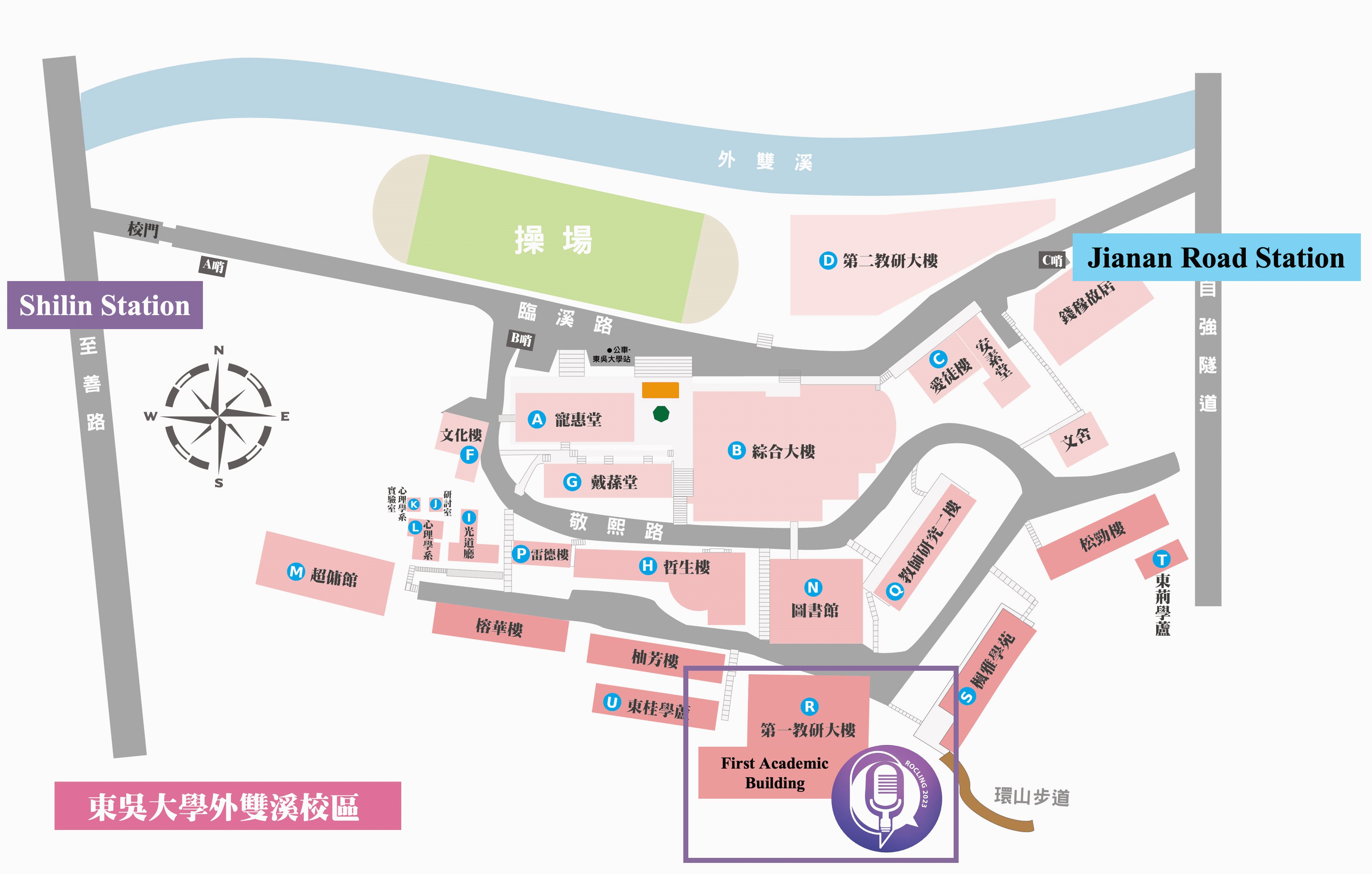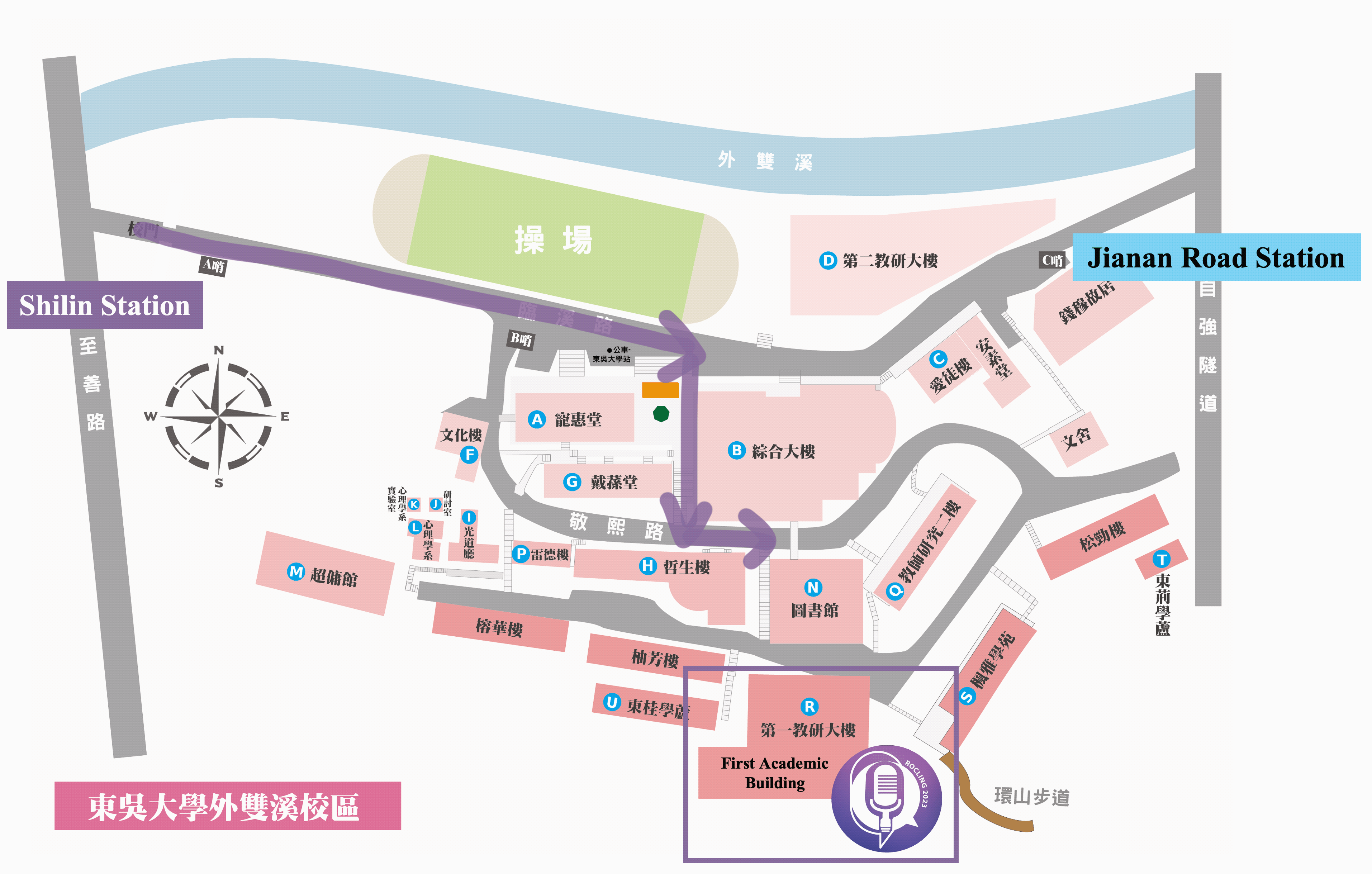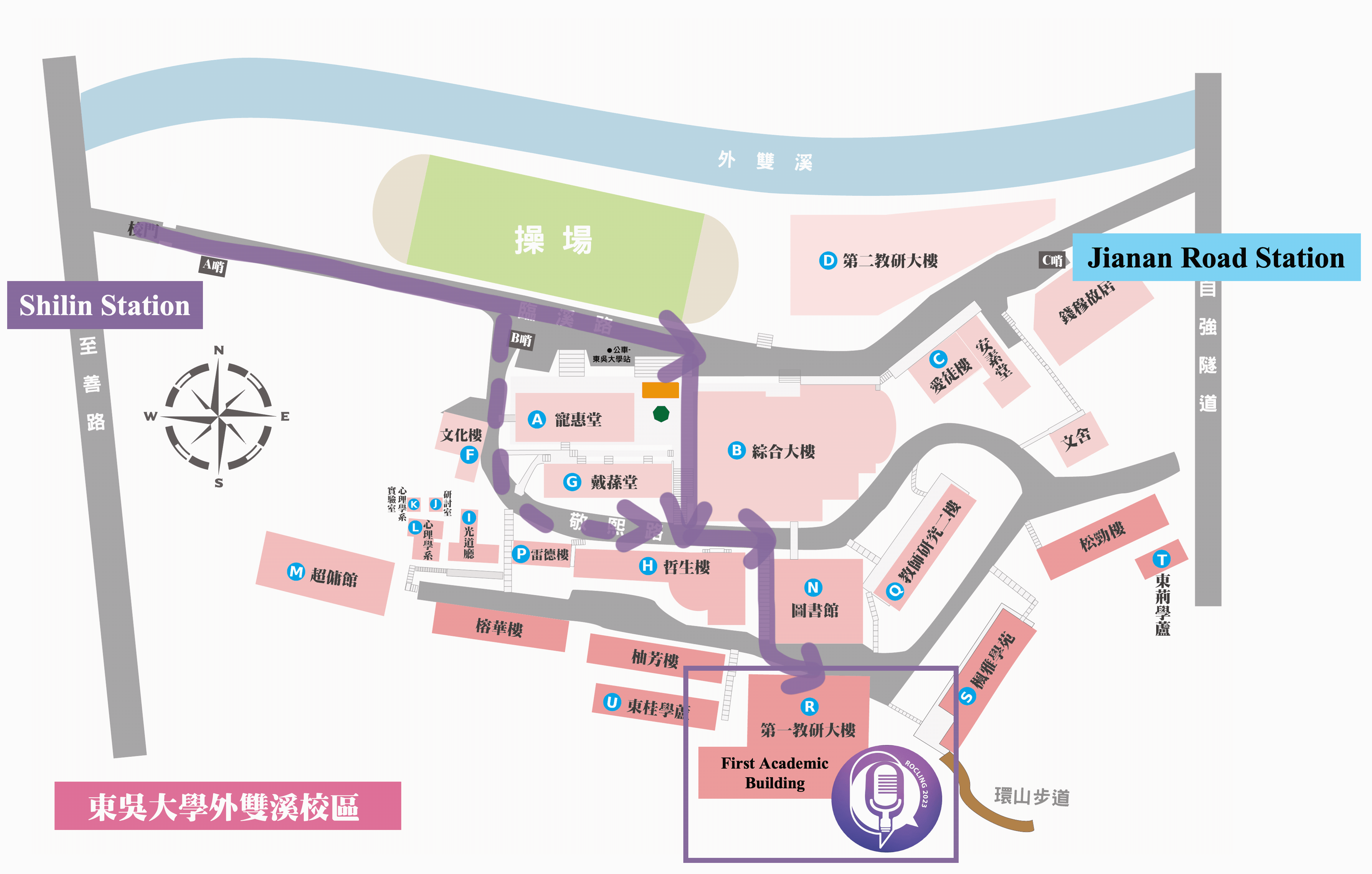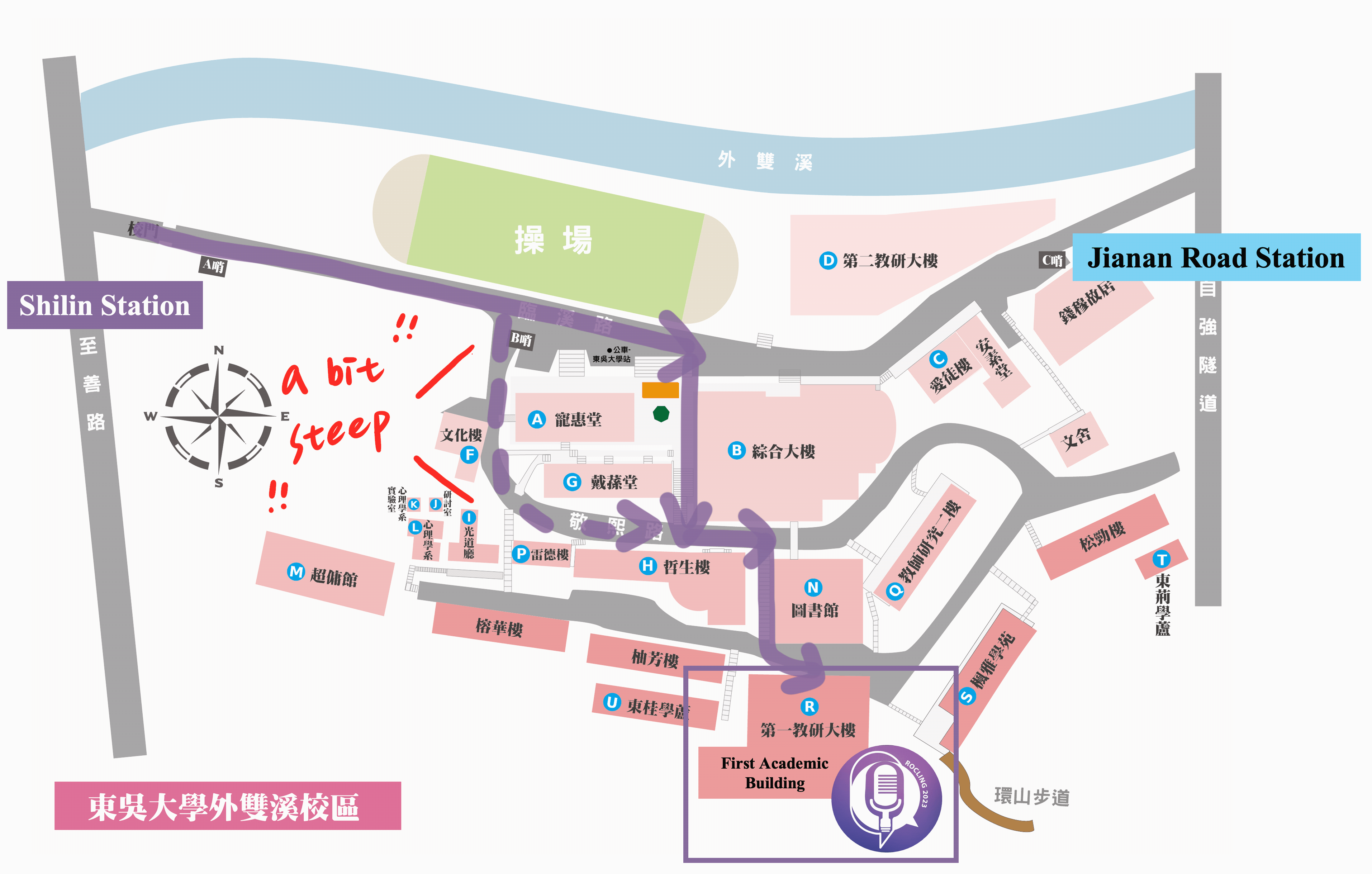
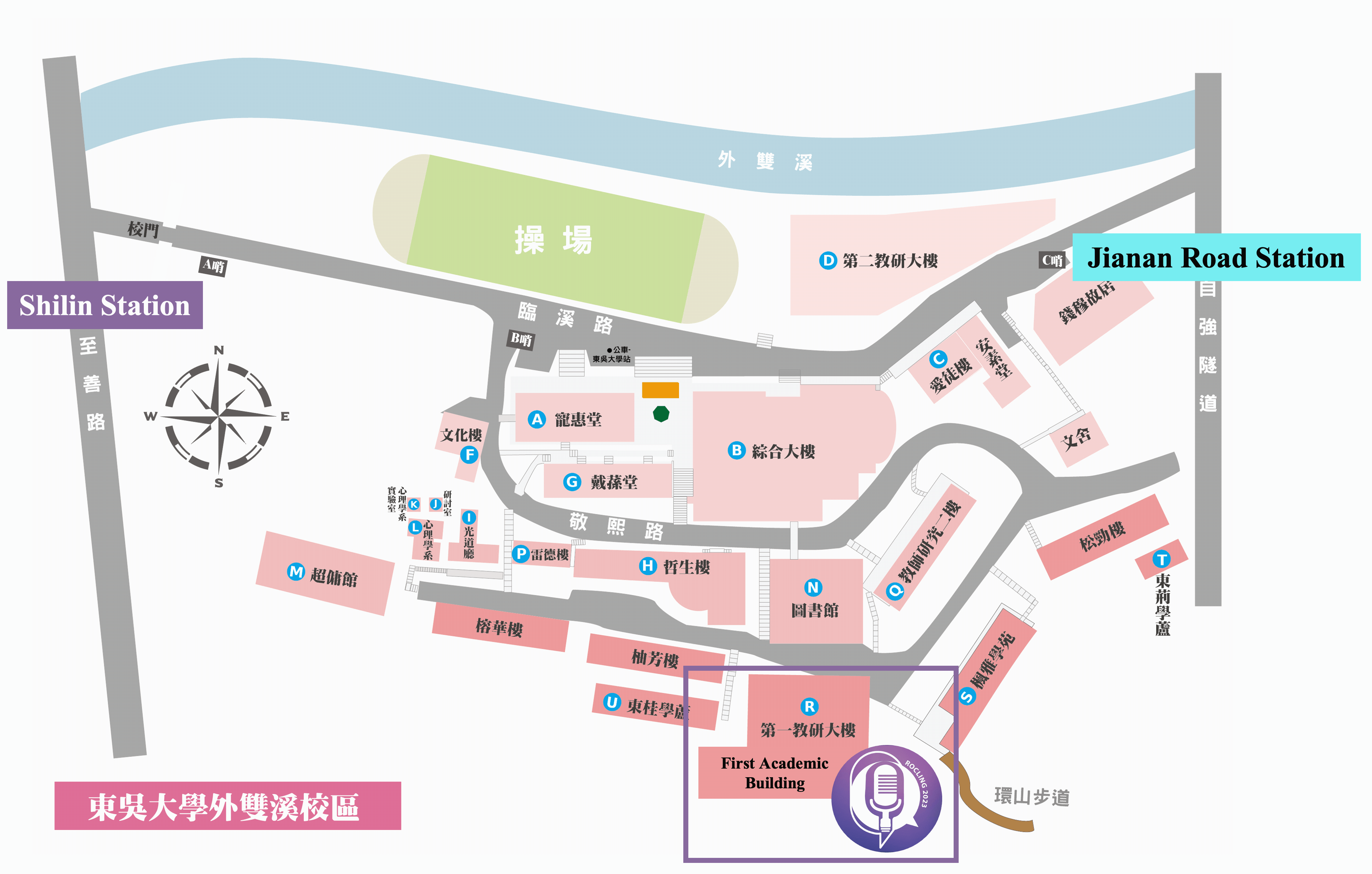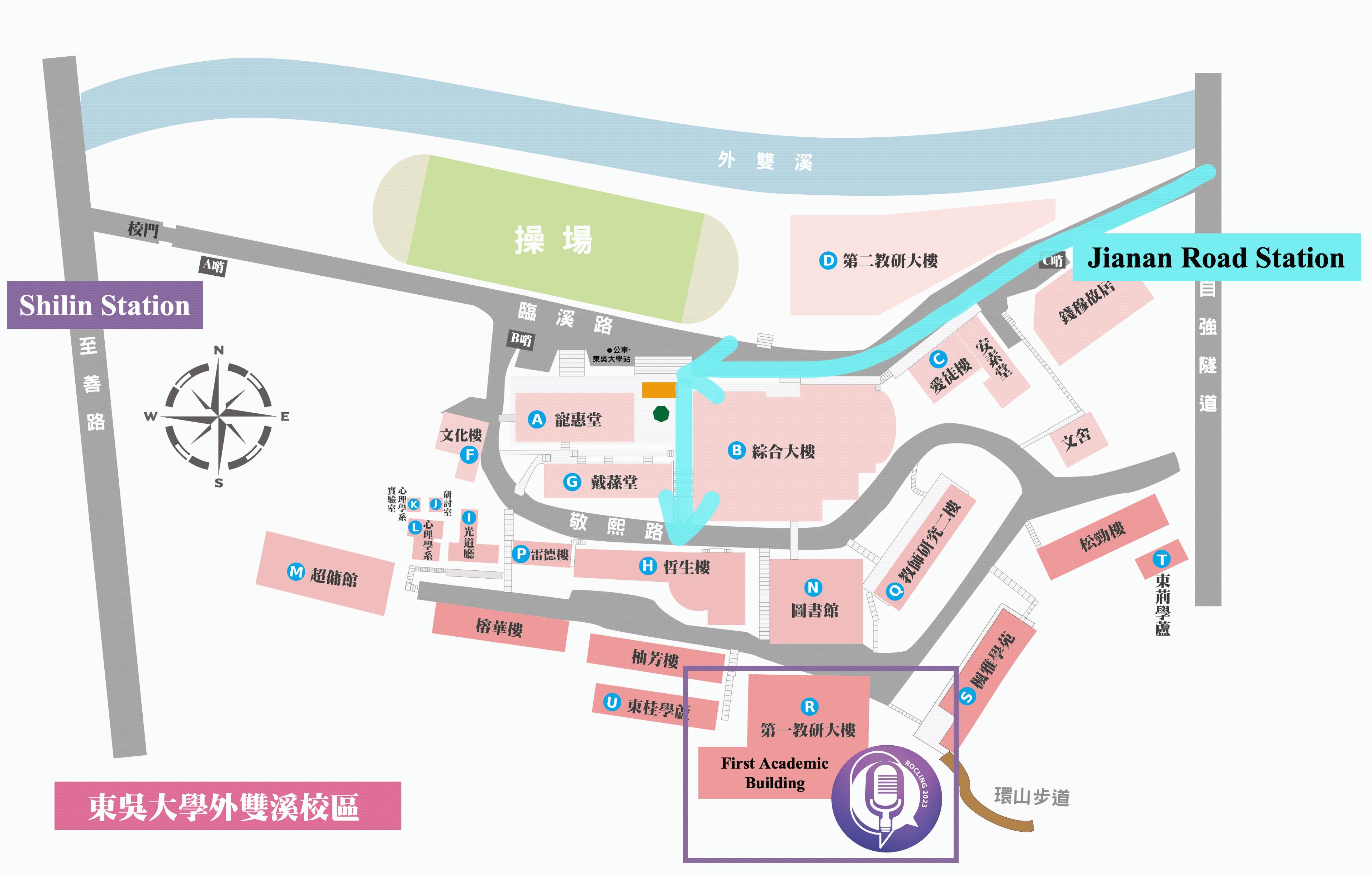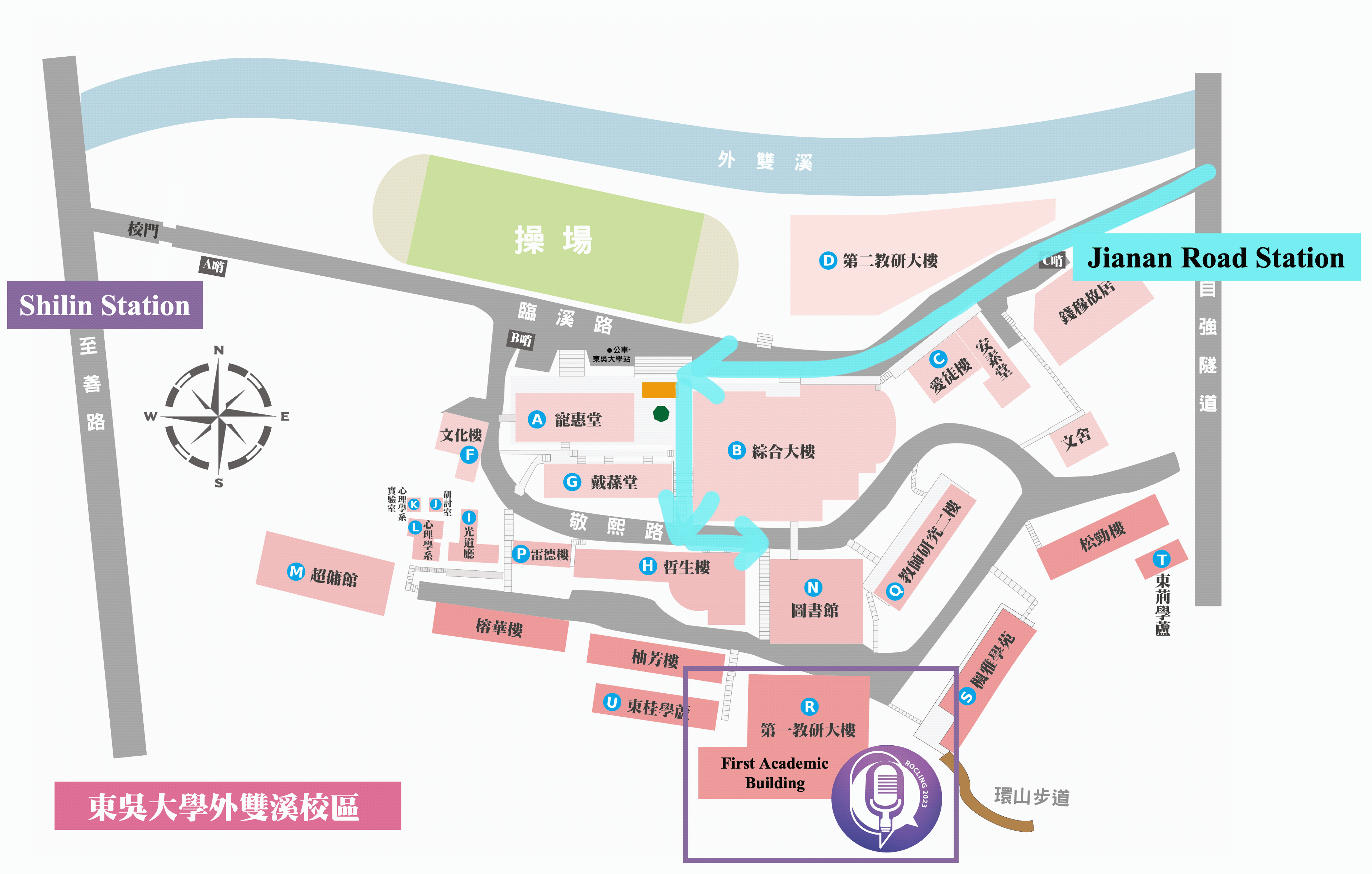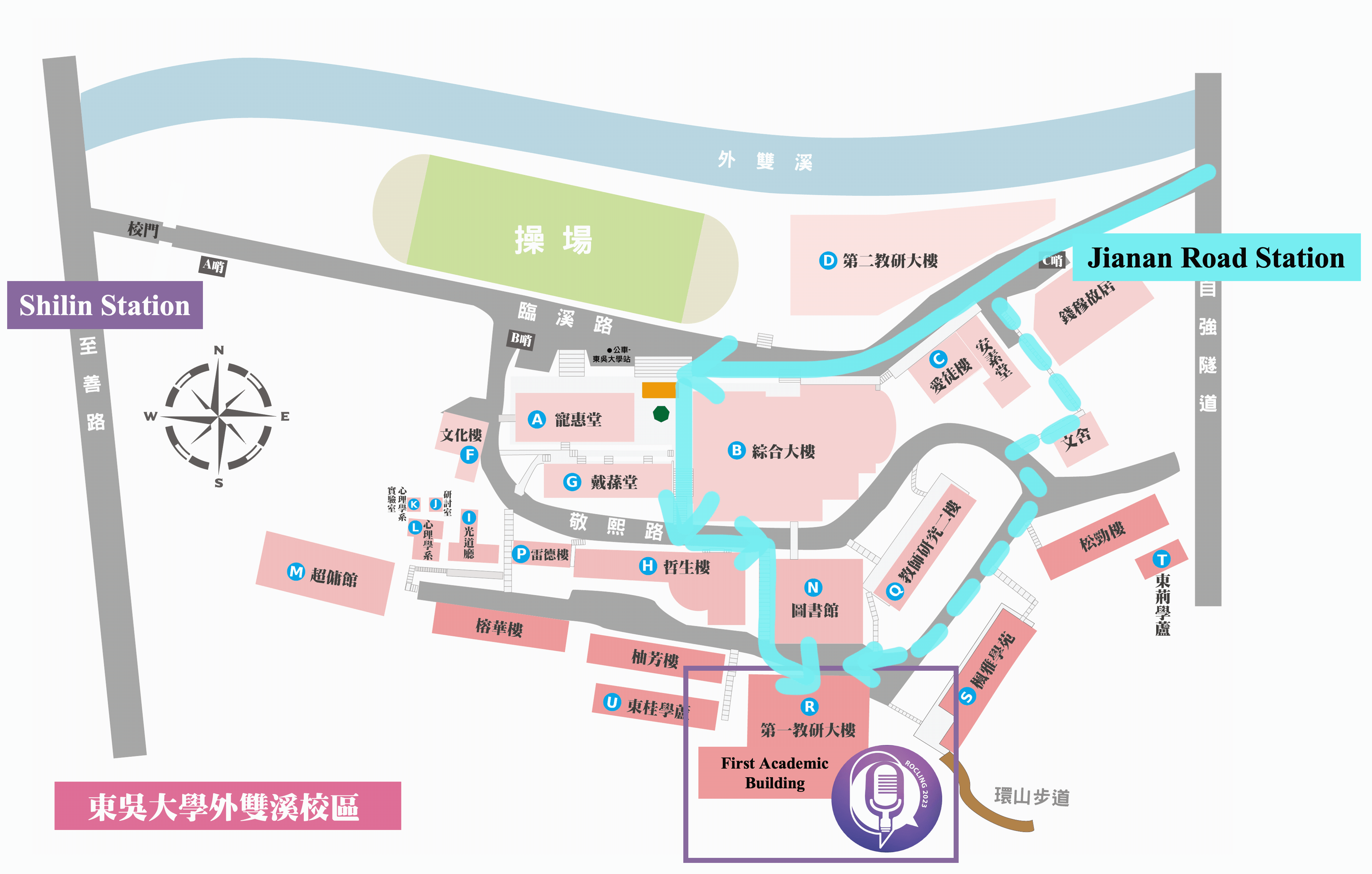
Conference Venue
Conference venue location info and gallery
First Academic Building, Waishuangsi Campus, Soochow University
東吳大學外雙溪校區
第一教學研究大樓
台灣台北市士林區臨溪路70號
No.70, Linhsi Road, Shihlin District, Taipei City 111, Taiwan
https://goo.gl/maps/jFinS5wdSVN31x8TA
By City Buses
- 255, 268, 304, 620, 645, minibuses 18 and 19, red 30 —Soochow University_Ch'ien Mu House stop
- 557 —Soochow University stop
By MRT
- Shihlin stop, transfer buses 255, 304, 620, minibuses 18 and 19, red 30 —Soochow University stop
By Train
- Taipei Station, transfer MRT to Shihlin stop, transfer buses 255, 304, 620, minibuses 18 and 19, red 30 — Soochow University stop
By Self Driving
- Sun Yat-sen Highway → Chongqing N. Rd. interchange (to Shihlin)→ Chongqing N. Rd. Sec. 4 → Bailing Bridge → Zhongzheng Rd. →Fulin Rd. → Zhishan Rd. → Waishuangsi Campus
- 學校停車場無對外面開放,請多加利用大眾交通工具
- 學校周圍於至善路設有路邊公有停車格
Hotel
Here are some nearby hotels

東吳大學學人招待所
-
No.70, Linhsi Road, Shihlin District, Taipei City 111, Taiwan
台北市士林區臨溪路70號 - 0.0 km from the Venue

Renaissance Taipei Shihlin Hotel
台北士林萬麗酒店
-
No. 8 Ln. 470, Section 5, Zhongshan North Road, Shilin District, Taipei City 111, Taiwan
台北市士林區中山北路五段470巷8號 - 1.7 km from the Venue

Grand Mayfull Hotel Taipei
台北美福大飯店
-
No.55, Lequn 2nd Rd., Zhongshan Dist., Taipei 10462, Taiwan
台北市中山區樂群二路55號 - 3.3 km from the Venue
F.A.Q
-
如果一次投稿多篇文章,該如何報名?
How do I register if I submit multiple articles at once?
每一篇投稿文章都必須至少有一名作者進行 Regular Register。也就是說,若您投稿兩篇文章,則必須分別為這兩篇文章進行 Regular Register。
There must be at least one author registered under the Regular registraction for each article submitted. As an example, if you submit two articles, both must be registered under the "Regular" registraction.
-
中華民國計算語言學學會是什麼?如果我要註冊 ROCLING 2023 一定要註冊中華民國計算語言學學會嗎?
What is ACLCLP Member? For ROCLING 2023, do I need to register as an ACLCLP member?
有關「中華民國計算語言學學會」之介紹與註冊請洽學會官網。若您不是學會成員也可以註冊 ROCLING 2023,詳情請參考註冊資訊。
For information and registration regarding the ACLCLP member, please visit the official website of the ACLCLP. You can still register for ROCLING 2023 even if you aren't a member of the ACLCLP. For more details, please refer to the registration information.
-
我該如何繳交註冊費用?
How can I pay the registration fee?
您可以使用郵政劃撥或是線上刷卡繳費,詳情請參考註冊資訊。
You can pay via postal transfer or credit card online.Please refer to the registration information for specific instructions.
-
如果我還有疑問該詢問誰?
If I have any questions, who should I contact?
- 註冊相關疑問,請聯絡何婉如小姐/Email: aclclp@aclclp.org.tw/Phone Number: 02-27881638。
- Shared Task I 相關疑問,請寄信至 rocling23-shared-task@googlegroups.com。
- Shared Task II 相關疑問,請聯絡:
- 楊小姐/Email: m31221123@nycu.edu.tw/Phone Number: 03-5712121#54554
- 白小姐/Email: pehsimju@nycu.edu.tw/Phone Number: 03-5712121#54555
- 投稿與其他疑問,請寄信至 rocling2023@gmail.com。
- For registration inquiries, please contact Ms. Ho at Email: aclclp@aclclp.org.tw/Phone Number: 02-27881638.
- For Shared Task I, please reach out to rocling23-shared-task@googlegroups.com.
- For Shared Task II, please contact:
- Ms. Yang at Email: m31221123@nycu.edu.tw/Phone Number: 03-5712121#54554.
- Ms. Bai at Email: pehsimju@nycu.edu.tw/Phone Number: 03-5712121#54555.
- For submission and other questions, please contact to rocling2023@gmail.com.





















